Atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process essential for life on Earth, because itGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) coolerMeasurements of greenhouse gases (GHGs), whether performed in the atmosphere, or over terrestrial or marine ecosystems, have led to a fundamental understanding of the Earth System during the last century Nevertheless, we still do not fully understand global greenhouse gas cycling Up to date measurements of GHG are still rare (as observation
1
What is the most common greenhouse gas in the atmosphere
What is the most common greenhouse gas in the atmosphere-Atmospheric Concentrations and Trends of Other Gases that Influence the Radiative Budget Ozone (O3) is an effective greenhouse gas in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere Significant decreases in total column O3 have been observed throughout the year during the last one to two decades, and at all latitudes except the tropics,This occurs when chemical reactions in the atmosphere produce or destroy greenhouse gases, including tropospheric ozone Indirect effects also occur when a gas influences atmospheric lifetimes of other gases or affects atmospheric processes like cloud formation that alter Earth's radiative energy balance by increasing Earth's albedo



Short Lived Climate Pollutants Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
There are two types of emissions that impact on the environment Greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), which can trap additional heat from the sun in the earth's atmosphere, causing the 'greenhouse effect' and climate changeCO 2 is the main greenhouse gas produced by motor vehicles In 17, the average combined CO 2 emissions for a new light vehicle sold inWhat are greenhouse gases?The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide because the more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the hotter the earth will become, changing
8 rowsGreenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon AtmosphericWater vapor The most abundant greenhouse gas, but importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate Water vapor increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide (CO 2) A minor but very important component of theHowever, the researchers found that all of these methods for greenhouse gas removal would not only reduce greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, but, on balance, they would also make our lives better
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenatedGreenhouse Gas Concentrations Graphing Tool Instruments at air sampling stations around the world have been checking the amounts of different gases in Earth's atmosphere for decades Many stations have instruments mounted at the top of tall towers to measure the abundance of gases in air in real time In some locations, scientists orAnd gases persist for different amounts of time in the atmosphere



Greenhouse Gases List Global Warming Contributors
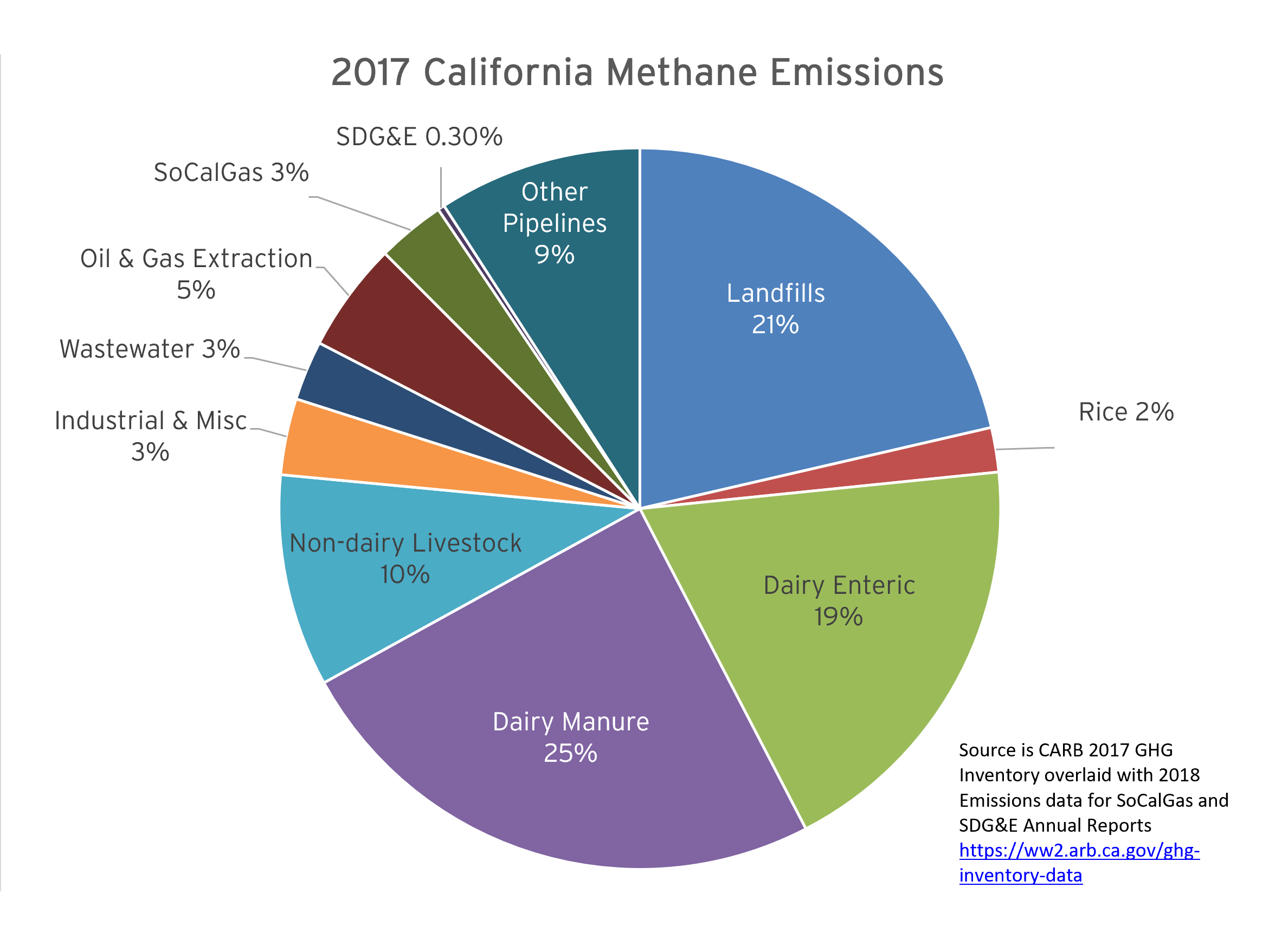



Sources Of Methane Emissions Socalgas
Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuels Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere are naturally regulated by many processes that are part of the global carbon cycle The flux, or movement, of carbon between the atmosphere and the earth's land and oceans is dominated byThe ratio of water component of the greenhouse effect to the CO 2 component is about 159 to 1 This means that the water vapor content of the atmosphere has to only fall from 041 percent to 0407 to wipe out the greenhouse effect of all the CO 2 in the atmosphere Given this sensitivity to the water vapor content it is clear that we really do not know whether the greenhouse gasSome of these gases (like methane) are considerably more shortlived in the atmosphere than CO 2, persisting for decades rather than centuries Such complications are often dealt with through the concept of global warming potential (GWP), which takes into account both the radiative properties of a particular greenhouse gas molecule and the




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb heat energy and emit it in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth's surface and lower atmosphere warm Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth's surface and lower atmosphereWater vapor is naturally present in the atmosphere and has a strong effect on weather and climate As the planet gets warmer, more water evaporates from the Earth's surface and becomes vapor in the atmosphere Water vapor is a greenhouse gas, so more water vapor in the atmosphere leads to even more warming265–298 Fluorinated gases A group of gases that contain fluorine, including hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride, among other chemicals These gases are emitted from a variety of industrial processes and commercial and household uses and do not occur naturally




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
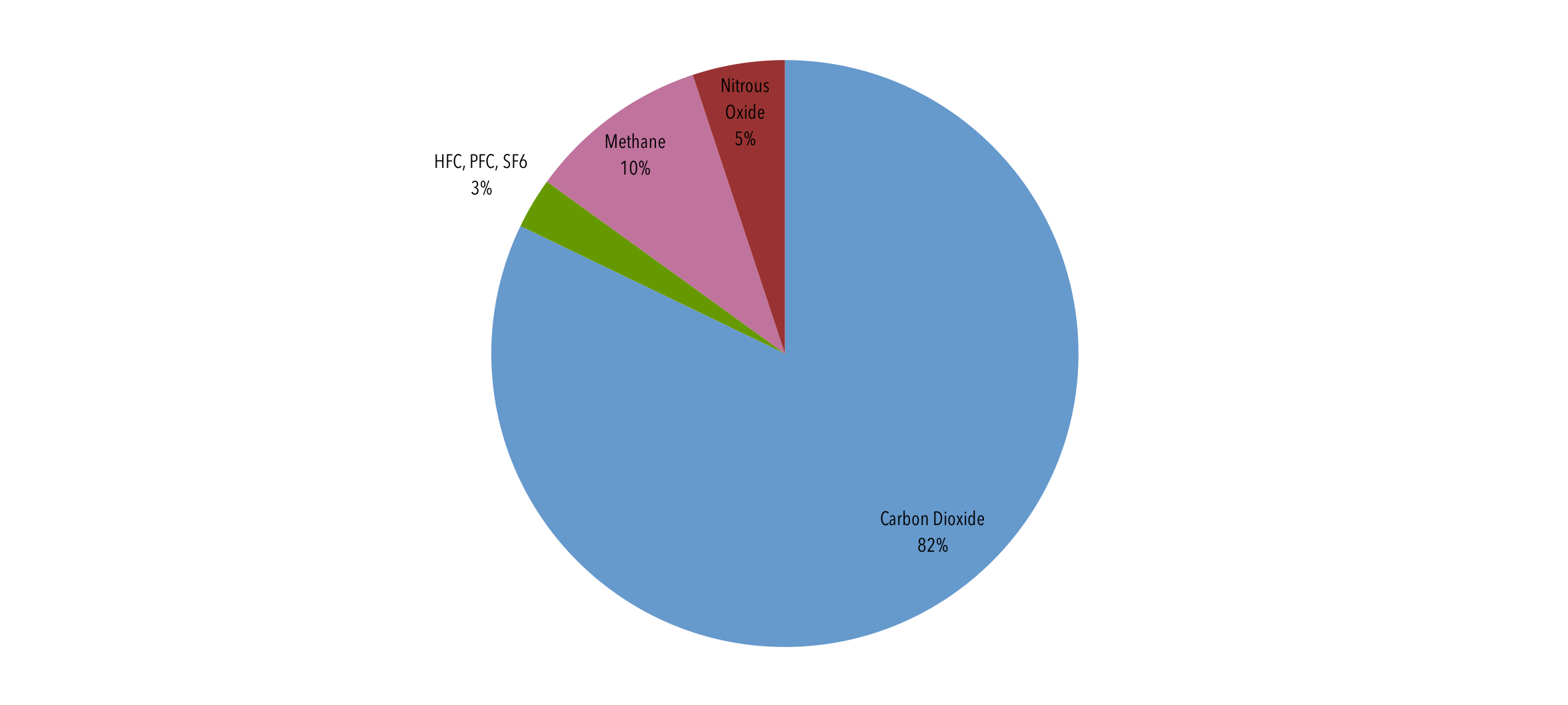
Additional trace gases produced by industrial activity that have greenhouse properties include nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and fluorinated gases (halocarbons) The latter includes sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs)These greenhouse gases are used in aerosol cans and refrigeration All of these human activities add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, trapping more heat than usual and contributing to global warming Effects of Global Warming Even slight rises in average global temperatures can have huge effectsSince measurements first started at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, atmospheric levels of CO 2 have risen from 315 ppm in 1958 to over 400 ppm today Concentrations are expected to stay above 400 ppm for many generations, because CO 2 can remain in the atmosphere for hundreds of years CO 2 is a longlived greenhouse gas responsible for roughly 65 percent of the total
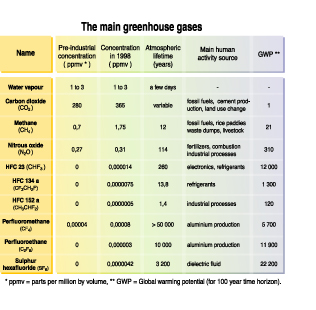



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal
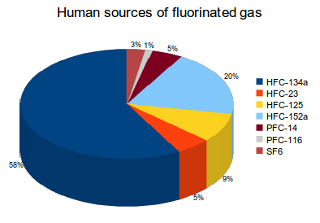



What Are High Global Warming Potential Gases What S Your Impact
The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can both absorb and reradiate much of the outgoing heat energy The atmospheric concentrations of some greenhouse gases are being affected directly by human activities namely carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and synthetic gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)Greenhouse gases reflect infrared radiation, so some of the heat leaving the Earth bounces off the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and comes back to the Earth's surface This is called the "greenhouse effect," in a comparison to the heattrapping glass on a greenhouse The greenhouse effect is not a bad thingThis graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributors




Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectLet's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and ResourcesComparing greenhouse gases All greenhouse gases absorb energy, but different gases have different effects on warming Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide remain in the atmosphere for long enough to allow them to mix together As a result, the gas concentrations are about the same around the globe, regardless of the source or location of the emissions
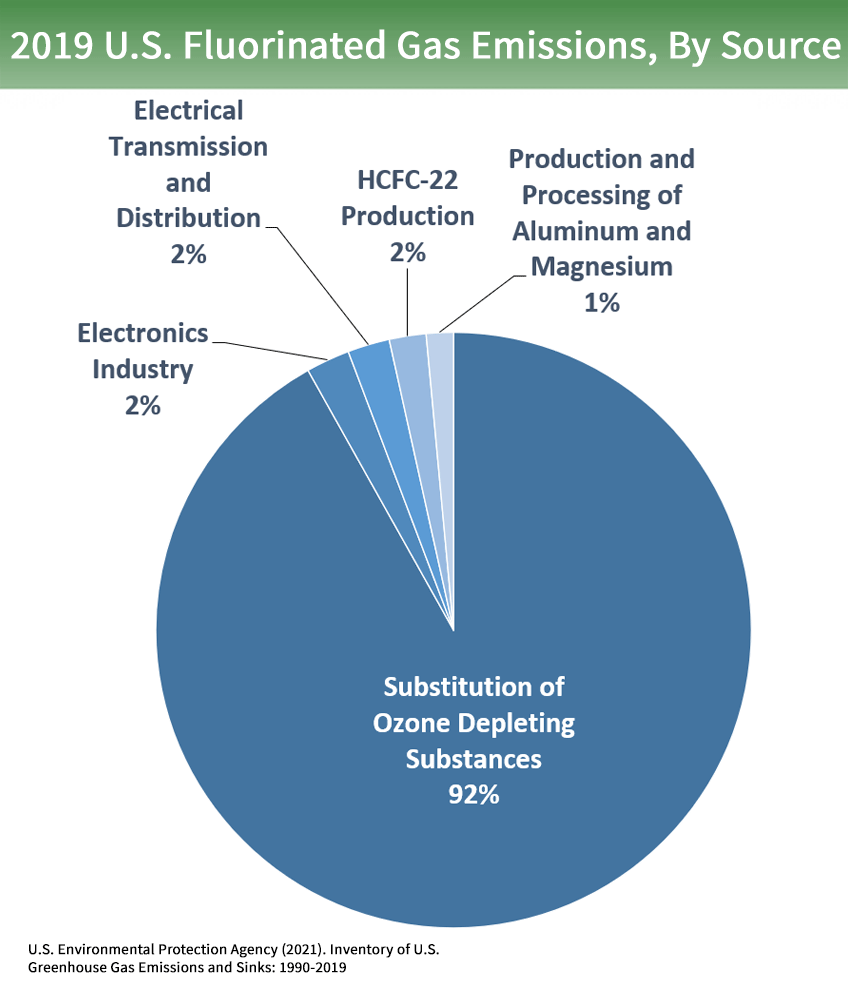



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
By increasing the heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect, which ultimately leads to global warming Related 10 signs that Earth's climate is off the railsWater vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide ChlorofluorocarbonsGreenhouse Gases The three most common types of greenhouse gases are Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, and coal), solid waste, trees and wood products, and as a result of other chemical reactions such as making cementCarbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and stored when it is absorbed




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky The trails are formed by soot and water vapor from the plane engines which burn keroseneTwo of the top countries on this list, China and India, are experiencing rapid economic growth Also on the list are the United States and European Union members—developed countries that have historically emitted and continue to emit greenhouse gases at high levels It is important to note that these ten countries produce a majority of global emissionsMajor greenhouse gases are Carbon dioxide Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Heat Transfer In The Atmosphere Physical Geography
The post – and the AGGI – mentioned carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and other gases, but failed to mention the biggest contributor to global warming plain old water vapor "I want to comment that the waydominant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is not mentioned, namely water vapor," writes Ken Saunders of Pacific PalisadesSelect Text Level 4 th Grade 6 th Grade 8 th Grade 12 th Grade The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gasesCarbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq) try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions Two things make this more complicated the gases have different 'strengths' of warming;
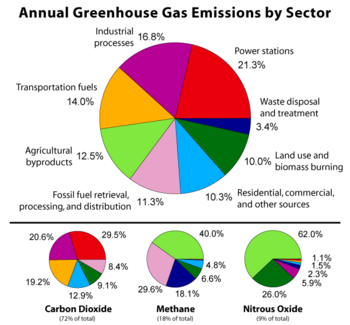



Greenhouse Gas New World Encyclopedia



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas which remains in the atmosphere for less than a decade, was 260% of preindustrial levels in 19 at 1 877 parts per billion The increase from 18 to 19 wasThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
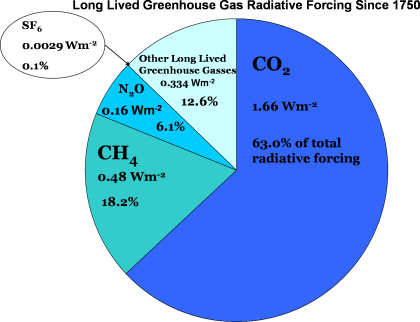



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory
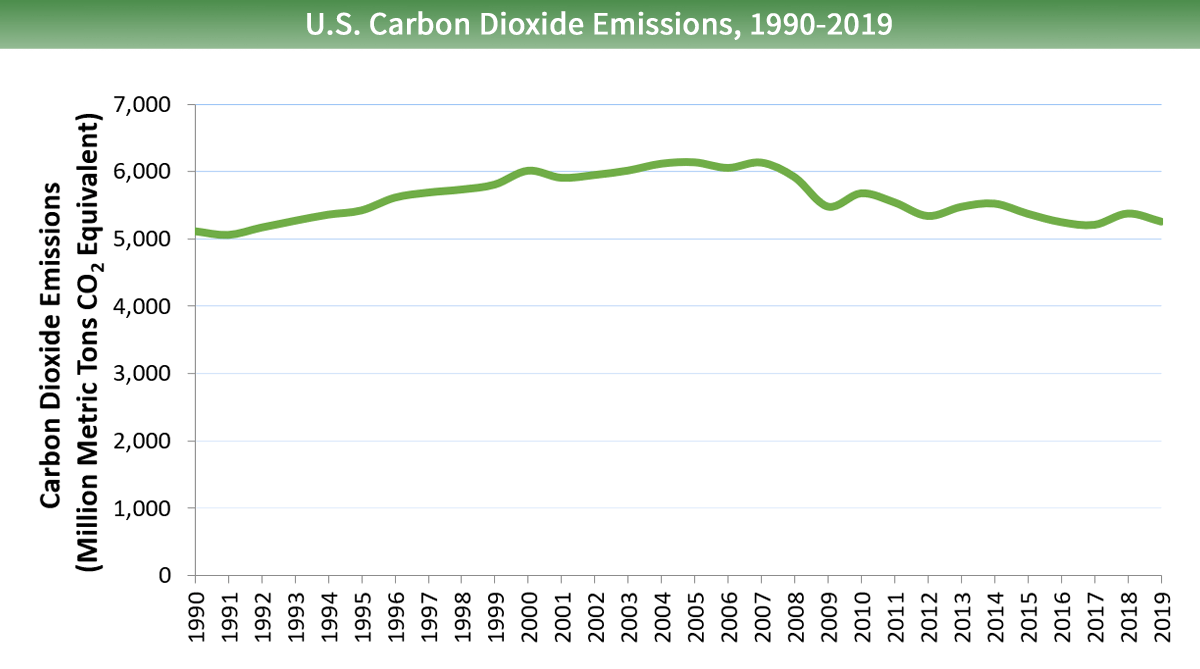



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



1




Greenhouse Gasses Definitions 1
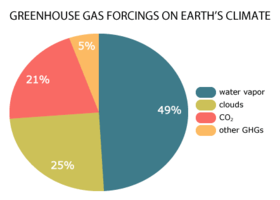



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Solved 8 List 5 Trace Gases That Have Been Associated With Chegg Com




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
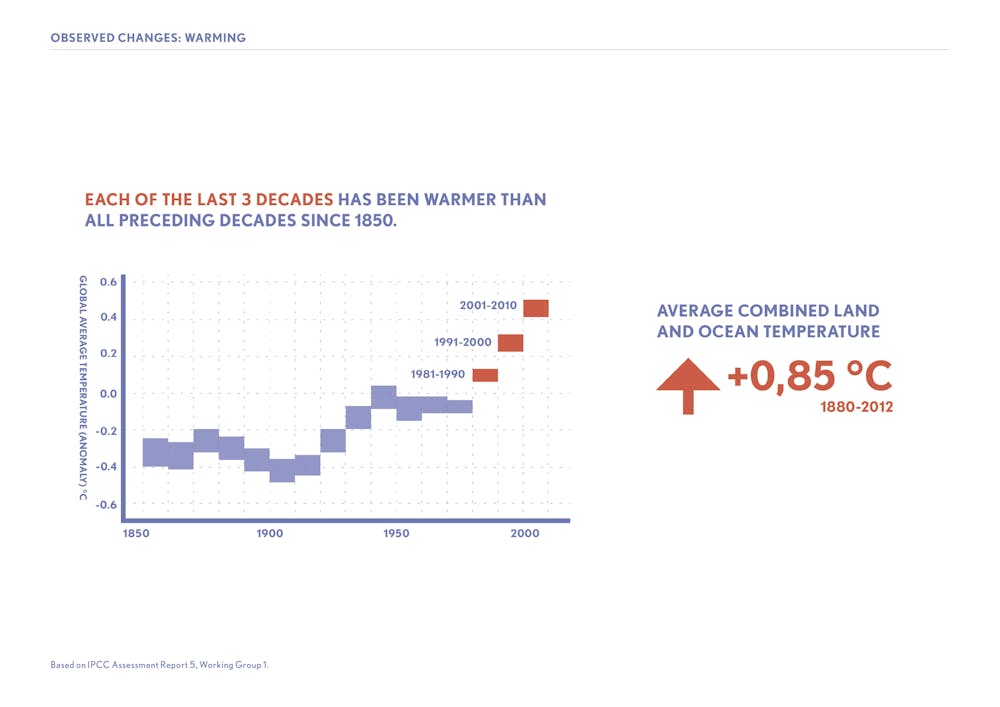



What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today
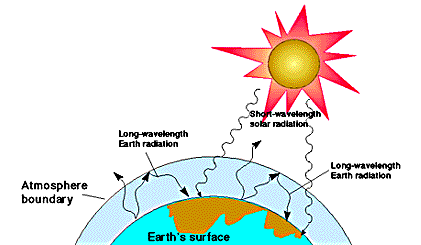



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Short Lived Climate Pollutants Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
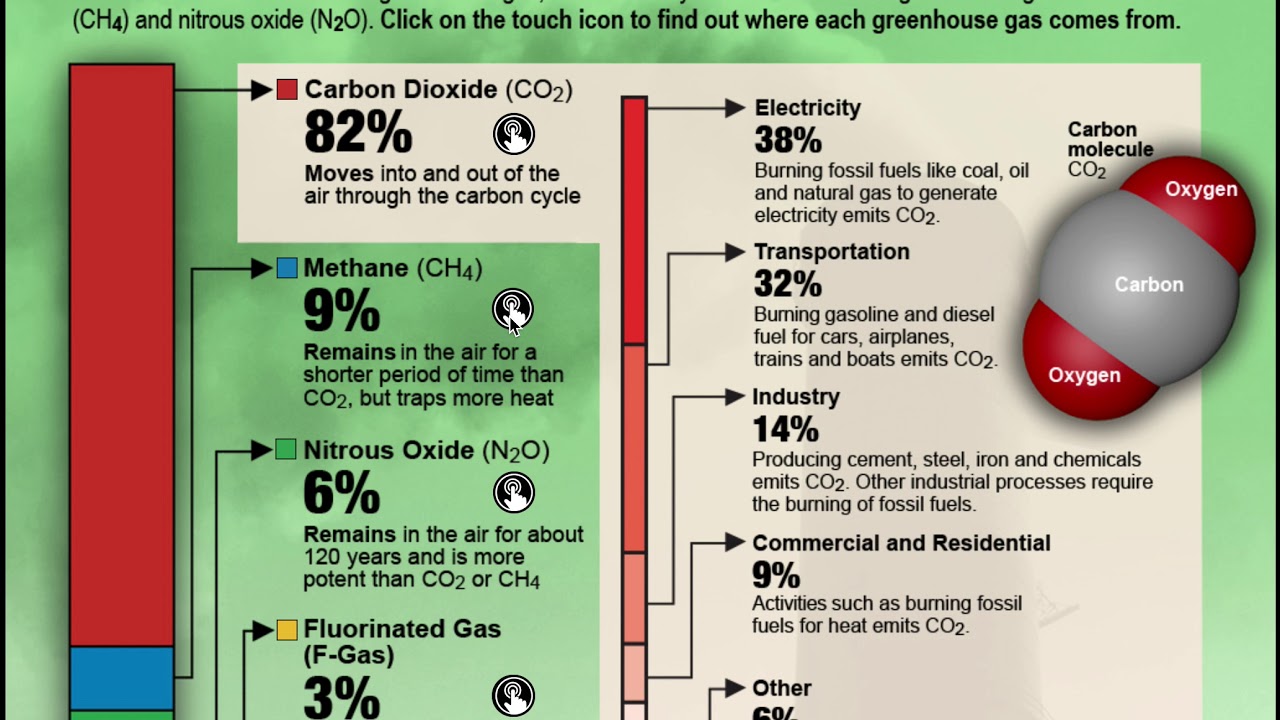



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica
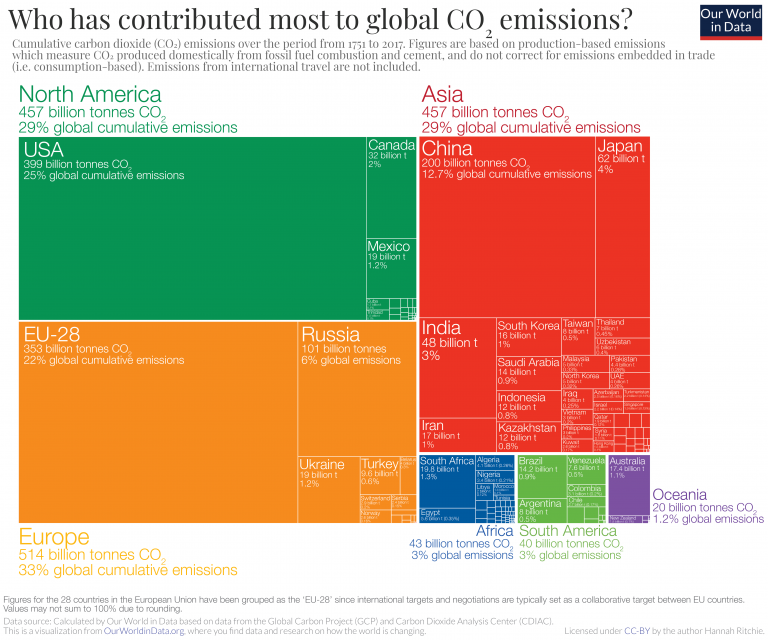



Who Has Contributed Most To Global Co2 Emissions Our World In Data




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
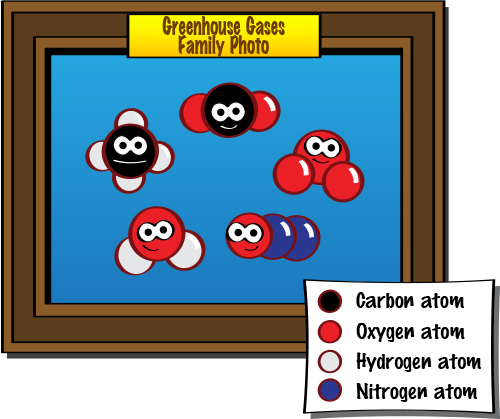



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids



What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora



Annual Ghg Index Aggi
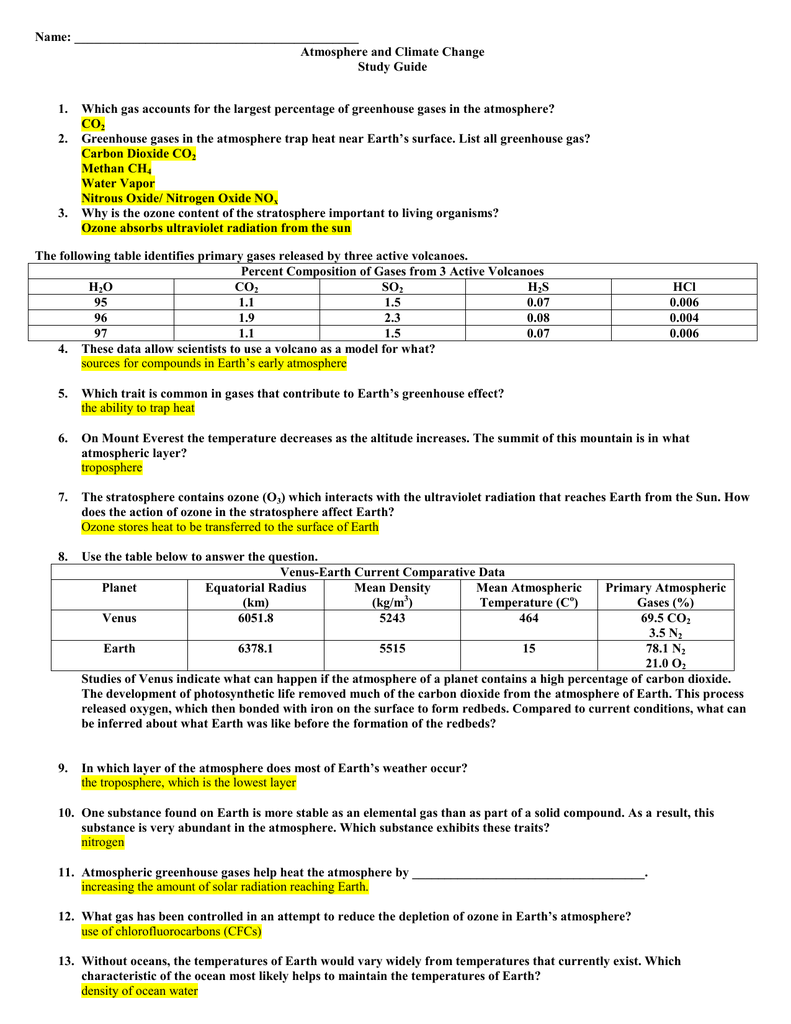



Which Trait Is Common In Gases That Contribute To Earth S
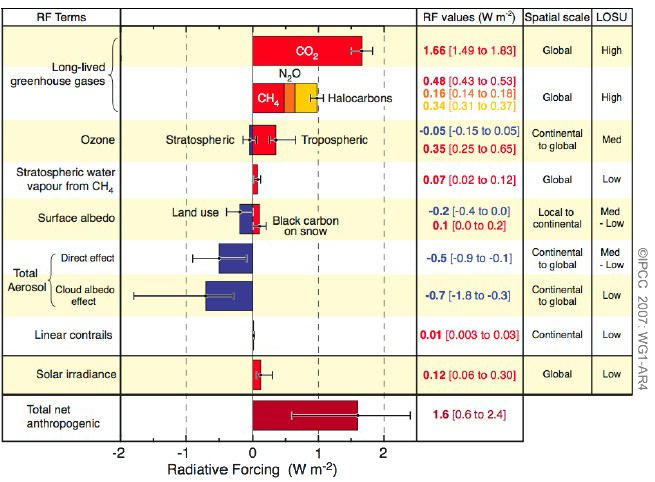



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
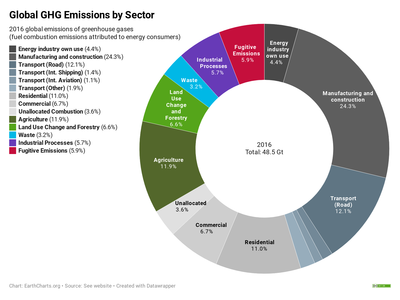



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Ipcc List Of Greenhouse Gases Wikipedia




Solved Which Of The Following Is Not An Anthropogenic Source Chegg Com




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
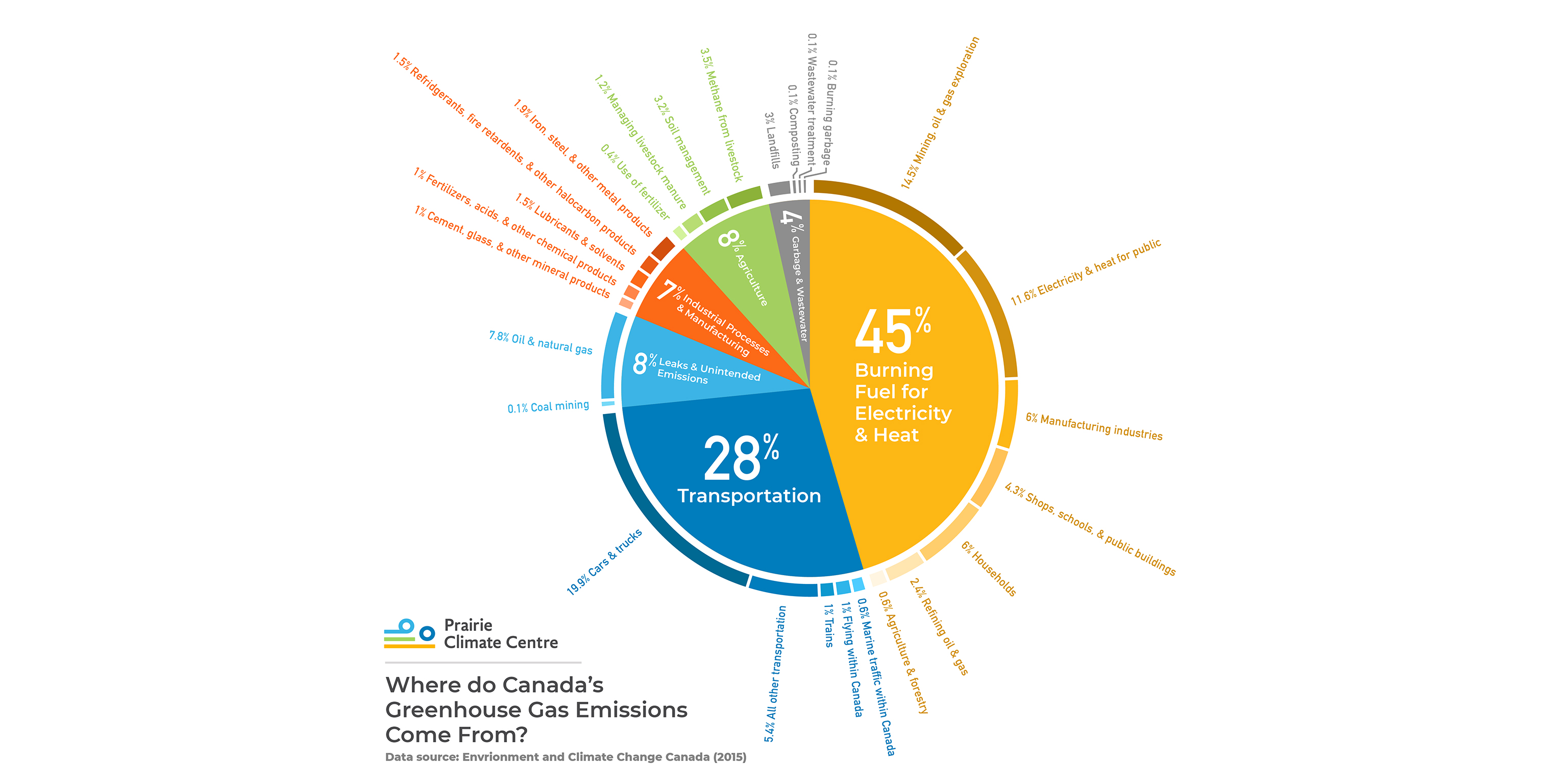



Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Solved Explain The Greenhouse Effect List 3 Important Chegg Com



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Which Nations Are Most Responsible For Climate Change Environment Theguardian Com




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram
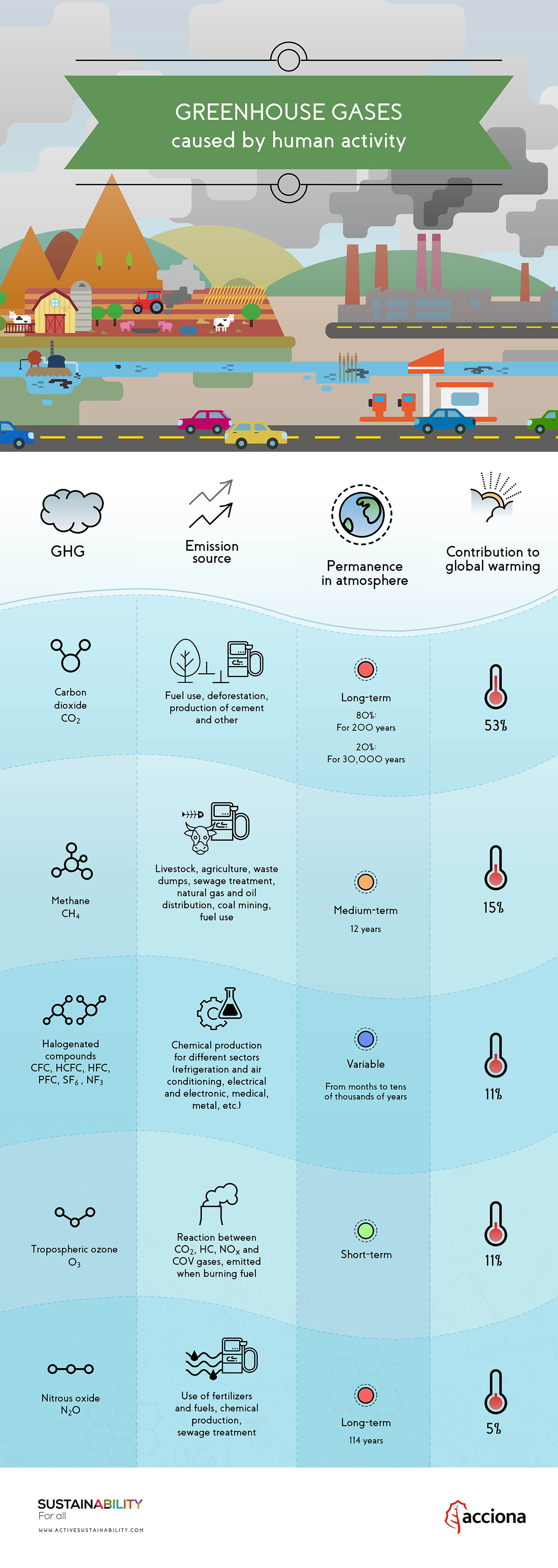



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming




Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium



Annual Ghg Index Aggi
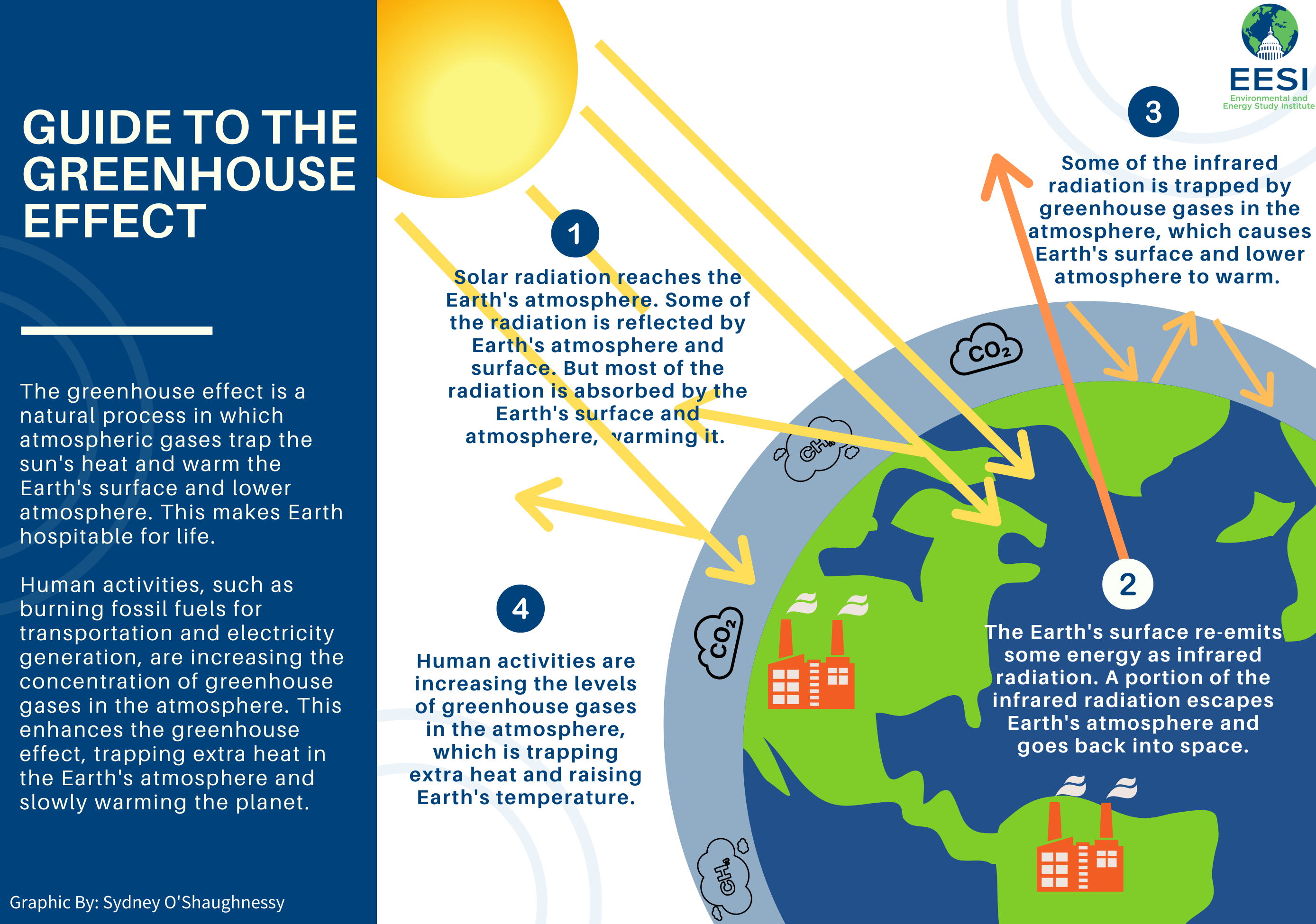



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi



Ozone Layer




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



3




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
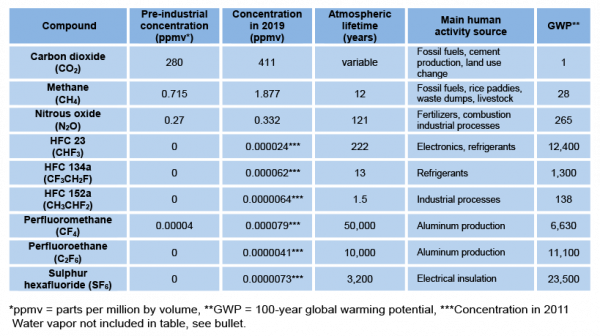



Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
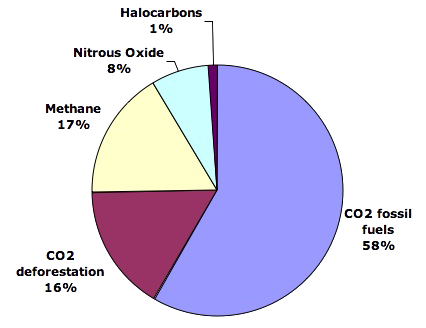



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
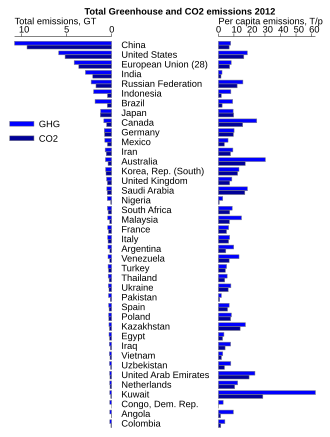



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



1
/521928855-58b5c1875f9b586046c8ee0e.jpg)



Worst Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere




The Main Greenhouse Gases Climate Change
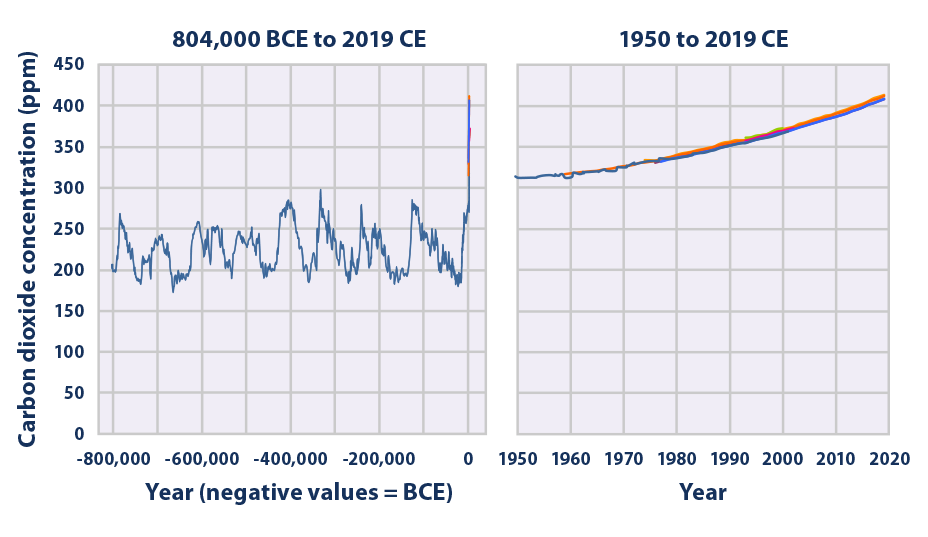



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
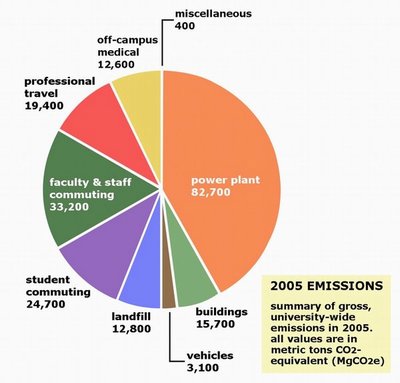



Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




List Of Greenhouse Gases Worldatlas




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
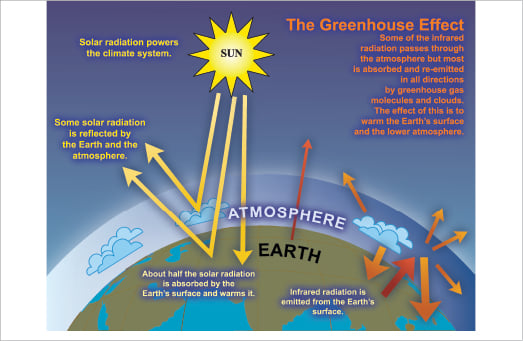



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
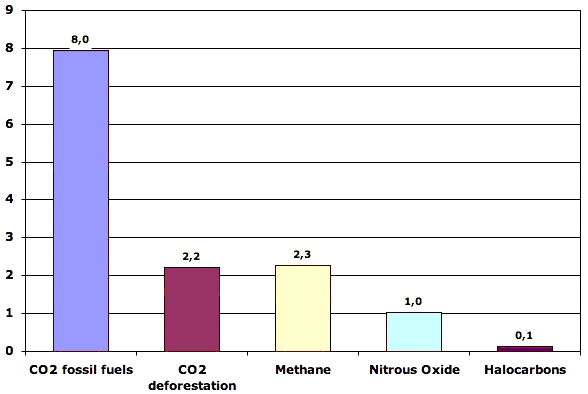



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿